PPC advertisers running Google Shopping ads typically choose a brand, margin, or category-based structure for their campaigns. These approaches are effective for broader advertising across a large inventory. Managing tens or hundreds of thousands of SKUs poses a challenge for advertisers, making it hard to focus on individual products.
Still, delving into SKU-level details is crucial to uncover hidden potential, address wasted budget, or identify specific products affecting overall category performance. To deal with product data at scale, consider implementing product scoring.
What is product scoring?
Product scoring involves assigning numerical values to products based on various performance indicators. This rating reflects a product’s potential or current market success.
Using product scoring, you can systematically choose which products to emphasize in your marketing and sales efforts, focusing on those with the strongest potential for advertising success.
For an effective product scoring system, several metrics play pivotal roles:
Sales velocity
- This parameter gauges the speed at which a product is purchased over a set duration. Products selling swiftly typically earn higher scores, signaling market appeal.
Customer insights
- Valuable insights gathered from customer reviews and ratings are indispensable.
- Products receiving positive feedback score higher, indicating their appeal to prospective buyers.
Profit margins
- Product scoring places significant emphasis on products with lucrative profit margins because they contribute more to the advertiser’s bottom line.
Conversion rates
- Measure how effectively customer interest is transformed into sales. High-scoring products are often those that achieve robust conversion rates.
Aligning with market trends and demand
- Advertisers who align their product offerings with market trends and consumer demands are likely to achieve higher product scores.
Inventory turnover
- This measures a product’s sales and restocking cycle. Products that are consistently in demand and quickly restocked tend to score higher, indicating sustained market desire.
In addition, any product scoring model can be extended with numerous metrics, such as:
- Add to cart.
- Pricing info like average price or price competitiveness
- Bookmarked products.
- Preorder ratio.
This additional information might help in fine-tuning the scoring model.
Dig deeper: Margin-based tracking: 3 advanced strategies for Google Shopping profitability
Integrating product scoring into your marketing strategy: A step-by-step guide
Incorporating product scoring into your marketing strategy is a step toward more precise and effective Shopping campaigns.
Below are the essential steps and considerations to add product scoring into your marketing activities.
Step 1: Establish your product scoring criteria
Identify key metrics
- Identify the metrics from the list above that matter most for your products and market. Consider sales velocity, customer ratings, profit margins, conversion rates, market trends, and inventory turnover.
Create a scoring model
- Construct a method to assign scores to your products based on these identified metrics. This model can range from a straightforward numerical scale to a more nuanced weighted algorithm.
- A basic model could be a scoring system from 1-5; a product’s score is determined by adding the score of each metric for the product. You can implement a basic scoring system quickly, but it lacks the sophistication that can be achieved with a more advanced model.
- A more advanced model could be based on this formula:
Product Score = sales volume (share) x price competitiveness x demand x profit margins
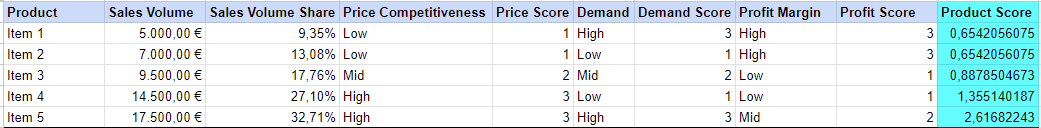
- Advertisers should test models. Some models might lead to more accurate decision-making results depending on the data quality.
There are almost no limits to the composition of metrics that contribute to the score. The most significant challenge may be aggregating data from multiple sources so that it can be analyzed. That leads to Step 2.
Step 2: Integrate data analytics
Use diverse data sources
- Tap into varied data sources, including sales records, customer feedback, market research, and digital footprints from online interactions.
Implement analytics tools
- Deploy sophisticated analytics tools capable of processing and interpreting this data to yield precise product scores. Opt for solutions that manage a lot of data and offer real-time analysis for adaptive scoring.
- On a small scale, information could be stored in a spreadsheet, which can be developed into an enterprise resource planning (ERP) based analytics database.
- Larger enterprises may start with a cloud-based data warehouse to aggregate all its product scoring data.
- Make sure to develop the necessary connectors or have an existing setup. For example analytics or ads data can easily be integrated. In contrast, Google Trends or ERP data might need an automated process to ensure timely and accurate data.
Step 3: Apply product scoring in marketing campaigns
Prioritize top-scoring products
- Allocate your marketing investments to products with the highest scores. This might mean increased advertising budgets, strategic placement in promotional materials, or special offers.
- Create automations to remove lower-scoring products or bring products without a score into a test cycle.
Step 4: Maintain and refine product scoring
Dynamic scoring updates
- Keep your product scores fluid, allowing them to evolve with shifting market trends, consumer preferences, and incoming data.
Ongoing scoring optimization
- Continually assess and fine-tune your scoring criteria and methods to ensure they stay pertinent and yield the most beneficial outcomes.
- Also, make sure to refine your scoring model and the metrics you use.
Step 5: Monitor results and glean insights
Track campaign efficacy
- Diligently monitor the performance of campaigns that feature high-scoring products, comparing their effectiveness against other campaigns.
Extract insights for future strategies
- Use the insights gleaned from these campaigns to inform and shape your future marketing strategies and product development decisions.
Challenges in implementing product scoring
Implementing product scoring involves navigating various challenges and adhering to best practices for maximum effectiveness.
The biggest challenge is likely data collection and management. As data accumulates, new tools and additional storage may be required.
Selecting the product scoring metrics you capture and store should be well thought out. Adding a new data source to the model means you’ll be losing historical context.
The product scoring must be aligned and updated frequently and reliably to supply quality data for marketing. This approach can only work if the data is correct.
Leverage product scoring for more effective campaigns
While developing and integrating a scoring system takes concerted effort, the rewards make it worthwhile. Product scoring provides a compass to guide your marketing dollars, advertising campaigns, and product development.
Balancing the focus between high and low scorers is important. While it’s essential to prioritize high-scoring products, lower-scoring products should not be completely overlooked, as targeted efforts can sometimes turn these products around.
Leveraging technology and automation for data processing and scoring reduces human error and increases efficiency.
Dig deeper: Google Merchant Center: Using product data to boost your retail efforts
from Search Engine Land https://ift.tt/a3FEkvM
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment