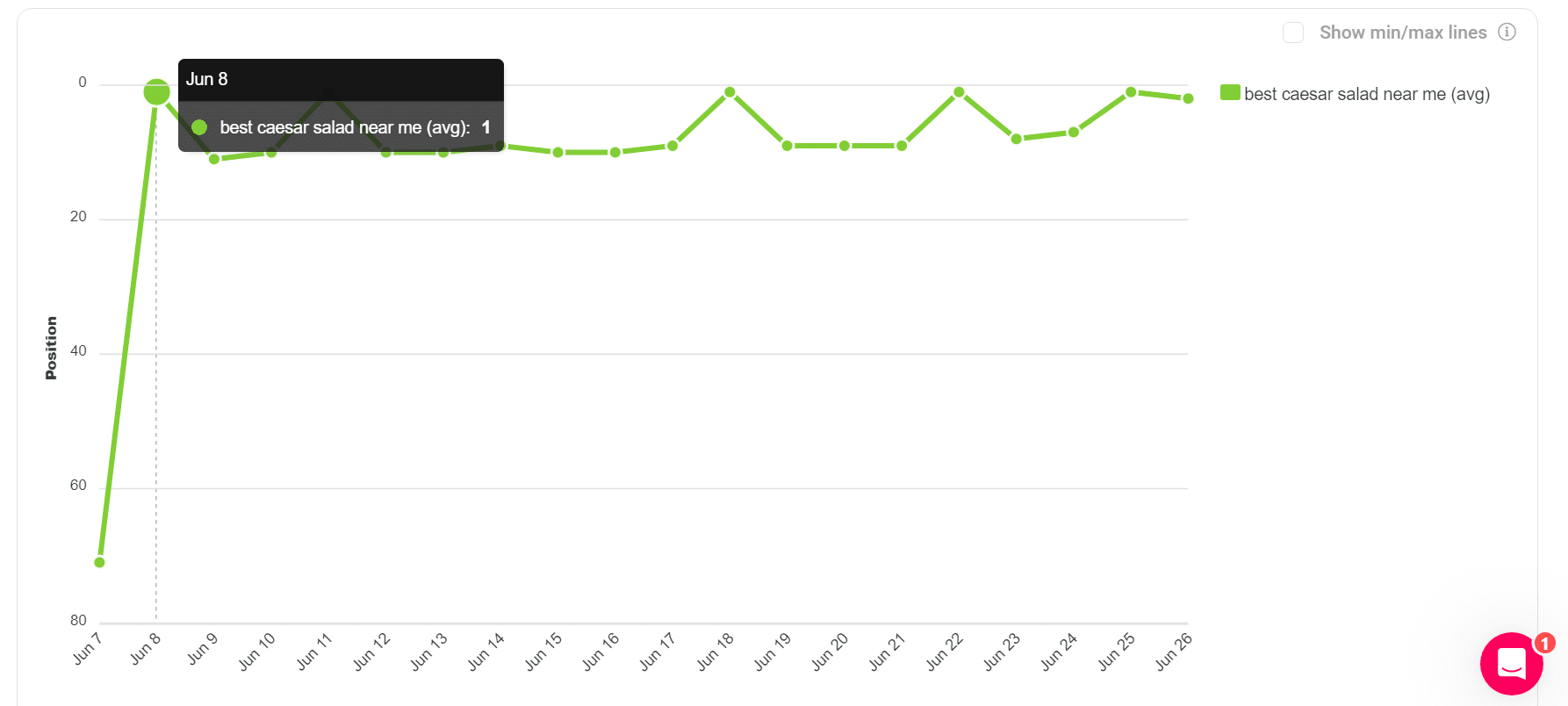
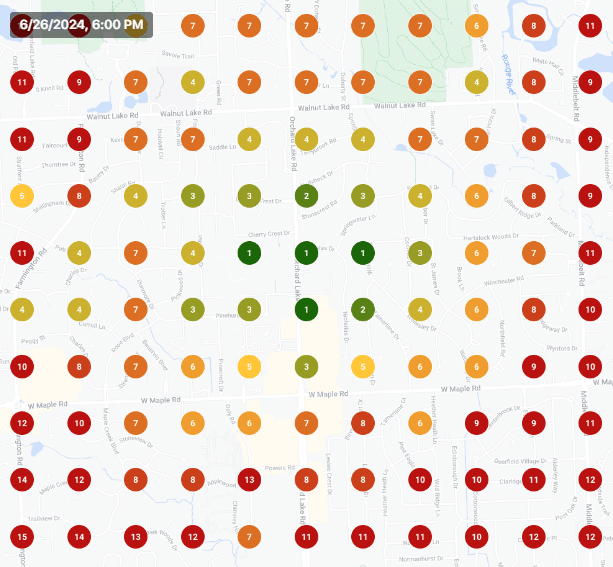
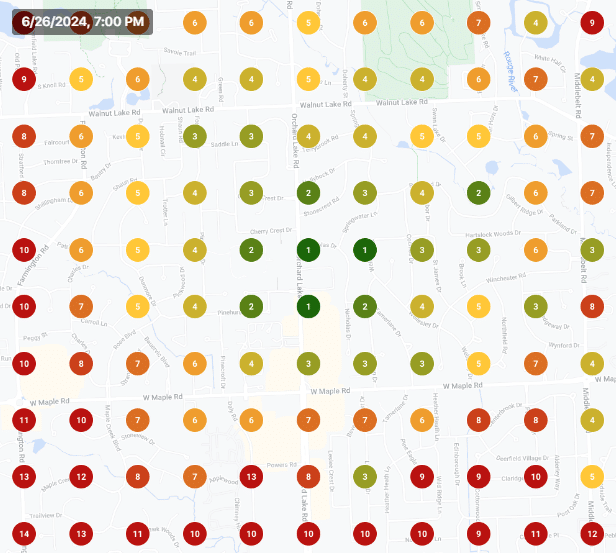
PPC advertising can be challenging, especially when your product or service falls into a sensitive or difficult category.
Whether you’re promoting pharmaceuticals, financial services, adult content or other regulated industries, advertising – especially on Google Ads – requires a balance of creativity, compliance and ethical consideration.
Google Ads remains one of the most powerful platforms for reaching potential customers. However, with great power comes great responsibility.
Advertisers in sensitive categories face unique hurdles, including:
- Strict policy restrictions.
- Heightened scrutiny.
- The constant risk of ad disapprovals or account suspensions.
Seasoned marketers might be frustrated by frequent suspensions, but these policies are in place to maintain a safer advertising platform.
Recent Google Ads data shows the extent of this effort. In 2023, they blocked or removed 5.5 billion ads and suspended 12.7 million advertiser accounts, nearly doubling their enforcement actions from the previous year. However, many businesses suffer from incorrect suspensions and misclassified compliance cases due to automated reviews.
This article aims to guide you through the advertising of sensitive categories on Google Ads. We’ll explore strategies to effectively promote your products or services while adhering to Google’s policies and maintaining high ethical standards.
Understand Google Ads policies
Google’s comprehensive policies ensure a safe and positive experience for users, advertisers and publishers. Knowing these policies is the first step to successful advertising in challenging niches.
Google Ads policies on sensitive categories
Google Ads policies are designed to protect users from harmful, deceptive or inappropriate content.
For sensitive categories, these policies are often more stringent and specific. They cover various aspects of advertising, including ad content, targeting and landing pages.
Key policy areas for sensitive categories often include:
- Restricted content: Products or services that can be advertised but with limitations.
- Prohibited content: Products or services that cannot be advertised at all.
- Editorial and technical requirements: Specific guidelines for ad copy, imagery and website content.
Commonly restricted and prohibited content
While the full list is extensive, some common examples of restricted or prohibited content include:
- Pharmaceuticals and healthcare products.
- Financial services (e.g., loans, cryptocurrencies).
- Gambling and games of chance.
- Adult content and services.
- Weapons and explosives.
- Alcohol and tobacco products.
- Political content.
Each category has its own set of rules. For instance:
- Pharmaceutical advertisers must be certified by Google and can only promote in certain countries.
- Financial services advertisers often need specific licenses and must provide additional disclosures.
The list of restricted categories is not exhaustive, as many subcategories and industries have unexpected policies.
For example, in the IT service industry, working on IT hardware may be prohibited unless you are a certified partner, which can be problematic for many computer repair shops or IT freelancers who lack certification from major manufacturers.
Why you must stay updated with policy changes
To stay compliant and effective in sensitive advertising categories on Google Ads, it’s essential to proactively monitor and adapt to policy changes.
Regularly review Google’s advertising policies, subscribe to their official policy updates and engage with industry forums or groups to gain insights on policy interpretations.
If you have a Google Ads representative, maintain open communication with them to escalate issues quickly.
Remember, policy violations can lead to ad disapprovals, account suspensions or even permanent bans. Staying informed and compliant is not just about avoiding penalties – it’s about building a sustainable, long-term advertising strategy on the platform.
Conduct thorough research
Thorough research is a must before launching your Google Ads campaign in a sensitive category. This groundwork will help you navigate policy restrictions, understand your audience and develop effective strategies within the given constraints.
Identify the specific restrictions for your category
When diving into Google Ads for sensitive categories, it’s crucial to go beyond just skimming the general guidelines. Dig into the specific policies that apply to your industry.
You’ll want to look out for any special requirements, like certifications or pre-approvals, that Google might need before you can run your ads.
Don’t forget to check for any geographical restrictions on where you can advertise. This can be a big deal, depending on your product or service.
Next, try to get a feel for how Google interprets and enforces these policies in real-world situations.
Take a look at the enforcement examples they provide and spend some time browsing industry forums to see what experiences other advertisers have had.
If you’re lucky enough to have a Google Ads rep, pick their brain for insights. They can be a goldmine of information.
Finally, don’t overlook the legal side of things. Make sure you’re up to speed on the laws and regulations in the markets you’re targeting.
Your ads and landing pages need to meet Google’s policies and adhere to the law.
It might seem like a lot of work upfront, but trust me, it’s way better than dealing with account suspensions or legal headaches down the road.
Understand the target audience and their needs
When you’re navigating the tricky waters of advertising in sensitive categories, understanding your audience becomes absolutely crucial.
Here’s the thing: with limited reach due to stricter policies and restrictions, every single interaction with a potential customer carries much more weight.
You can’t afford to cast a wide net and hope for the best. You need to make every impression count.
That’s why it’s important to dive deep into your target audience’s psyche. Crafting detailed buyer personas isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s essential.
You need to understand not just surface-level demographics but also your potential customers’ underlying motivations, concerns and online behaviors.
What specific pain points are they grappling with? How do they search for solutions?
These insights can help you create hyper-targeted ads that resonate on a personal level. Also, make sure to get the full picture of your target audience’s search behavior.
In sensitive categories, your audience might not be using the most obvious keywords but also a mix of alternatives, synonyms or abbreviations used in the industry.
Don’t underestimate the power of direct feedback, either. Surveys and interviews with your target audience can provide golden nuggets of information that might not be apparent from broader data analysis.
These firsthand insights can help you fine-tune your messaging to address specific concerns or highlight benefits that truly matter to your audience.
Lastly, mine your existing customer data relentlessly. Those customer service logs, reviews and FAQs are treasure troves of information. They reveal the real questions and concerns your audience has, allowing you to craft ads that speak directly to these issues.
Analyze competitors and their strategies within the constraints
Instead of fixating on copying what’s currently visible, focus on understanding the broader landscape.
Look at businesses offering similar products or services, but also consider alternative solutions that might be competing for your audience’s attention. This gives you a more comprehensive view of the market.
When analyzing competitor ads and landing pages, look for patterns in messaging and structure rather than specific tactics.
How are they communicating value while navigating policy restrictions? What themes seem to be consistent across multiple competitors?
This approach helps you understand the industry’s general direction without getting hung up on potentially non-compliant examples.
While it’s tempting to emulate competitors who seem to be pushing boundaries, always prioritize compliance.
If you notice competitors potentially breaking rules, use that as a reminder to double-check your own practices rather than as inspiration to follow suit.
Your goal should be to find ethical, compliant ways to stand out in a tightly regulated space.
Craft compliant ad content
Creating effective ad content for sensitive categories requires a delicate balance between compelling messaging and policy compliance.
Tips for writing ad copy that complies with Google Ads policies
When crafting ads for sensitive categories, navigating the fine line between effective marketing and policy compliance is crucial.
Familiarize yourself with prohibited terms in your industry and create a list of approved alternatives. Focus on highlighting factual, verifiable benefits without resorting to superlatives or unsupported claims.
Transparency is key. Be clear about your offering and include necessary disclaimers directly in your ad copy.
Maintain a professional tone throughout your messaging, avoiding sensationalism and using industry-appropriate terminology. This approach aligns with the seriousness of sensitive categories and helps build trust with your audience.
Make smart use of ad extensions to provide additional, compliant information. Sitelinks can offer more context, callouts can highlight key features or certifications and structured snippets can showcase your product categories or services.
Selecting appropriate visuals and media content
When creating visual content for sensitive category ads, aim to balance attractiveness with policy compliance.
Thoroughly review Google’s image policies for your specific niche, avoiding anything graphic or overly sensational. Always ensure you have proper consent to feature individuals in your visuals.
Focus on high-quality, relevant imagery that accurately represents your product or service. Consider using lifestyle images to provide context, but make sure they remain professional and appealing.
Don’t forget to incorporate necessary disclaimers or warnings directly into your visual content, ensuring they’re clearly legible.
When exploring different ad formats, such as responsive display ads or video content, proceed with caution. Every element must adhere to platform policies, from the opening frame to the closing shot.
Finally, leverage A/B testing to optimize your visual strategy. Create multiple versions of your ads with different images, then monitor their performance to identify what resonates best with your audience while maintaining strict compliance.
This data-driven approach allows you to refine your visual content strategy over time, maximizing impact within the bounds of platform regulations.
Examples of compliant ad content in sensitive categories:
- Pharmaceutical ad
- Instead of: “Miracle cure for all your ailments!”
- Try: “FDA-approved medication. May help manage [specific condition]. Consult your doctor.”
- Financial services ad
- Instead of: “Guaranteed approval for high-interest loans!”
- Try: “Personal loans available. Rates from X.XX% APR. Terms apply.”
- Adult content ad
- Instead of explicit imagery or text.
- Try: “Adult entertainment. Age-verified. Secure, discreet service.”
Design effective landing pages
Ensuring landing pages meet Google’s policy requirements
When it comes to landing pages for sensitive category ads, transparency and compliance are paramount.
Include comprehensive, accurate details about your product or service, with all the necessary disclaimers, terms and conditions.
Don’t shy away from clearly stating any limitations, risks or potential side effects associated with your offering. This upfront honesty builds trust with potential customers and helps you stay on the right side of advertising policies.
Make sure your business information is easily accessible. Display your company name, physical address and contact details prominently. Include clear links to your privacy policy and terms of service, typically in the footer.
For certain industries, consider adding a visible customer support phone number to further enhance credibility and meet specific policy requirements.
Pricing and billing information should be crystal clear. Display all costs upfront, including any recurring charges or additional fees. Explain your billing process in simple terms.
Avoid any hint of hidden charges or misleading pricing structures. These are quick ways to violate platform policies and consumer trust.
Lastly, pay close attention to industry-specific requirements. If you’re in financial services, include necessary licensing information and disclaimers.
For pharmaceuticals, ensure all claims are approved and include required warnings. Adult content requires robust age verification systems.
Dig deeper: PPC landing pages: How to craft a winning post-click experience
Provide high-quality, relevant content that aligns with the ad
When crafting landing pages for sensitive category ads, focus on creating a seamless, trustworthy experience.
Ensure your page content aligns perfectly with your ad claims, maintaining consistency in language and tone.
Provide comprehensive, valuable information about your offering, including FAQs and policy-compliant testimonials if possible.
Use clear, concise language throughout, avoiding jargon unless necessary. Organize content logically with headers and bullet points for easy digestion.
Incorporate trust signals like relevant certifications, security badges and reputable reviews to build credibility.
Leverage advanced targeting options
When advertising in sensitive categories, precise targeting becomes even more crucial. It helps ensure your ads reach the right audience while minimizing the risk of policy violations. Here’s how to leverage advanced targeting options effectively:
Utilize demographic and geographic targeting to reach the right audience
Set appropriate age restrictions based on your product and policy requirements to optimize targeting, ensuring adult content targets users 18 or older.
Use gender targeting for gender-specific products but avoid unfair discrimination. Employ geographic targeting to comply with regional regulations and exclude prohibited locations.
For financial or luxury products, target by income level to reach interested users while adhering to fair lending laws. Utilize parental status targeting for family-oriented products, ensuring content suitability and compliance.
- Website visitor remarketing
- Create lists based on specific page visits to target users who’ve shown interest.
- Exclude converters to avoid unnecessary ad spend.
- Customer match
- Upload customer email lists to re-engage past customers.
- Ensure you have proper consent to use customer data for advertising.
- Similar audiences
- Use this feature to find new users similar to your existing customers.
- Be cautious with sensitive categories to avoid targeting inappropriate audiences.
- Dynamic remarketing
- Show ads featuring products or services users have viewed on your site.
- Ensure all product images and descriptions comply with policies.
- Remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA)
- Adjust bids for past visitors when they search for relevant keywords.
- Use this to bid more aggressively on high-intent searchers.
Dig deeper: How to combine Google Ads with other channels to retarget, nurture and convert
Use custom intent audiences to target users based on their search behavior
- In-market audiences
- Target users actively researching or considering products/services in your category.
- Be selective with in-market categories to ensure relevance and compliance.
- Custom intent audiences
- Create audiences based on keywords, URLs and apps your ideal customer might search for or use.
- Focus on intent signals that indicate genuine interest without crossing policy lines.
- Affinity audiences
- Target users based on their long-term interests and habits.
- Choose affinities that align with your offering while respecting privacy concerns.
- Life events targeting
- For relevant products/services, target users going through specific life changes.
- Ensure your messaging is sensitive and compliant when using this option.
Tips for compliant and effective targeting in sensitive categories
To optimize ad targeting, use layered targeting to combine multiple methods for specific audience segments, ensuring ads reach the most appropriate users.
Implement exclusions with negative keywords and audience lists to avoid inappropriate contexts, regularly updating them.
Use contextual targeting in display campaigns to ensure ads appear in relevant, brand-safe environments. Apply frequency capping to limit ad exposure and prevent fatigue.
Schedule ads based on the time and day when your audience is most receptive. Regularly review and optimize targeting performance, staying alert to any policy or regulatory changes that might impact your strategy.
Spammy advertising methods to steer clear of
Black hat marketers use deceptive tactics to bypass platform policies. These include cloaking, redirect chains, multiple accounts, coded language and URL shorteners. Some also use rapid ad rotations or slight variations to evade detection.
While these methods may temporarily work, they violate terms of service and can lead to permanent account suspensions, legal issues, and reputational damage. These practices are risky, unethical and strongly discouraged by advertising platforms and professionals.
Cloaking is a deceptive technique where different content is shown to search engines or ad reviewers compared to regular users. It detects when a page is accessed by a crawler or review system and shows compliant content, while regular users see potentially non-compliant content. This is often achieved through:
- IP detection: Identifying known IP ranges used by search engines or ad platforms.
- User-agent sniffing: Checking the browser or device information to spot crawlers.
- JavaScript-based cloaking: Using scripts to alter page content based on user behavior.
Advertisers using cloaking promote policy-violating products or boost rankings with hidden, keyword-stuffed content. This serious violation often leads to immediate account suspension or blacklisting. As detection methods improve, cloaking becomes increasingly risky and unsustainable.
Such techniques are especially dangerous for real, established companies:
Long-term consequences for legitimate businesses
While black hat marketers often operate with disposable websites and temporary accounts, real businesses have much more at stake:
- Brand reputation damage: Once exposed, black hat tactics can severely tarnish a company’s reputation. In today’s interconnected digital world, news of unethical practices spreads quickly and can be nearly impossible to overcome.
- Loss of customer trust: Consumers value authenticity and transparency. Discovering that a trusted brand engaged in deceptive practices can lead to a mass exodus of customers and long-lasting negative sentiment.
- Permanent platform bans: Major advertising platforms like Google Ads or social media sites may permanently ban offending businesses. This can be catastrophic for companies relying on these channels for customer acquisition.
- Legal ramifications: Depending on the nature of the deception, businesses might face legal consequences, including fines or lawsuits from misled customers or regulatory bodies.
- SEO penalties: Search engines can apply severe penalties or completely de-index sites caught using black hat SEO techniques, effectively erasing years of legitimate SEO efforts.
- Financial losses: Beyond immediate revenue drops, companies may face long-term financial repercussions from damaged reputation, legal fees and the cost of rebranding efforts.
- Industry blacklisting: In some sectors, being caught using black hat techniques can lead to industry-wide blacklisting or loss of crucial partnerships.
- Decrease in employee morale and retention: Ethical employees may leave when they discover their company engages in deceptive practices, leading to brain drain and internal turmoil.
Unscrupulous marketers may quickly abandon a project after being caught, but legitimate businesses have established customer bases and long-term goals.
The risks of unethical marketing far outweigh any potential short-term gains for companies focused on sustainable growth and customer trust.
Instead, ethical marketing practices ensure steady, reliable growth and protect valuable assets like reputation and customer loyalty.
If a client is considering unethical tactics, emphasize the long-term consequences. For a legitimate business, it’s never worth it to engage in unethical marketing.
from Search Engine Land https://ift.tt/0LJhjn7
via
IFTTT